Difference between revisions of "Preference:Alias"
(→How It Works: explicit example to offer clarification) |
(/inform howto paste mirc codes etc) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| − | Match commands in examples are only suggestions. | + | Match commands in examples are only suggestions. Users may put whatever they want. Some examples (e.g., /hug, /inform, /colors) can be tested in http://staging.mibbit.com/url/RV7Y9I (demo widget). |
===Hugs=== | ===Hugs=== | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
'''Command''' | '''Command''' | ||
| − | + | chr(2)chr(3)0,4 INFORM: chr(2)chr(3)1,0 $1- | |
| + | ( chr(2)=\u0002 bold toggle, chr(3)=\u0003 mIRC color prefix, you can load skin 42c110f3cbbaea489c0b0e40a40e6e18 into the /manager/ or d689a3c0594106af0184d7684e7ee2af into the main client, then copy and paste the codes into your own aliases or directly into the input bar). | ||
| − | '''Usage:''' /inform It's very cold out there | + | '''Usage:''' |
| + | /inform It's very cold out there | ||
'''Output:''' | '''Output:''' | ||
Revision as of 00:24, 15 May 2009
Aliases are user set commands that reference other commands so that they do not have to repeat themselves each time they want to use a specific line. As they are preferences, they can be set for widgets also.
Contents
How It Works
MATCH - This is the first word on the line, that we're matching against. It can start with / but doesn't have to.
COMMAND - This is what you want to do if the alias matches.
Bear in mind that the first match will trigger, so if you have duplicate matches, only the first will be used. The match is also case insensitive.
| | | Separate multiple commands (with a space at each side) |
| # | The current channel |
| $N | (Where N is a number) - replace this with the Nth word from the input |
| $$N | Same as above, but if there is no such word, only ignore this command, not the whole alias |
| $N- | replace with all words from N onward (i.e. $3- would take the third word and all following it) |
| $N-M | replace with all words from N to M (i.e. $1-5 would take the first 5 words) |
| $+ | suppress the space between words |
| $me | Your current nickname |
| /say | Say something on the current channel |
You can have a .,!? after $me, and you can have a # before any of the $N commands.
Examples
Match commands in examples are only suggestions. Users may put whatever they want. Some examples (e.g., /hug, /inform, /colors) can be tested in http://staging.mibbit.com/url/RV7Y9I (demo widget).
Hugs
| This example contains helpful information that is not part of the other examples. |
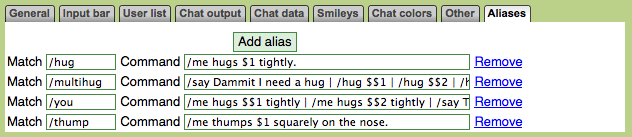
Match:
/hug
Command
/me hugs $1 tightly.
Now if you write "/hug jenny", you'll see:
* yournick hugs jenny tightly.
You can use an alias you declared before it. An example of this is the /multihug command:
Match:
/multihug
Command
/say I need a hug :( | /hug $$1 | /hug $$2 | /hug $$3 | /say phew! That felt good. I'm glad I'm in # and not in #nohugs!
Now write "/multihug jenny cloe" you'll see:
mynick: I need a hug :( * mynick hugs jenny tightly. * mynick hugs cloe tightly. mynick: phew! That felt good. I'm glad I'm in #mychannel and not in #nohugs!
Inform
Match:
/inform
Command
chr(2)chr(3)0,4 INFORM: chr(2)chr(3)1,0 $1-
( chr(2)=\u0002 bold toggle, chr(3)=\u0003 mIRC color prefix, you can load skin 42c110f3cbbaea489c0b0e40a40e6e18 into the /manager/ or d689a3c0594106af0184d7684e7ee2af into the main client, then copy and paste the codes into your own aliases or directly into the input bar).
Usage:
/inform It's very cold out there
Output:
INFORM: It's very cold out there
Bans
Quiet Bans
A quiet ban is a type of ban that makes it so that the user can do anything except for speak.
Match:
/qb
Command
Unreal Version: /mode # +b ~q:*!*@ $+ $1 Freenode Version: /mode # +q $1 $+ !*@*
Usage:
Unreal Version: /qb nickname!username@hostname Freenode Version: /qb nick
Output:
yourNick has banned q:nickname!username@hostname
Show bans
Match:
/sb
Command
/mode # +b
Usage:
/sb
Output:
The output is dynamic, but it shows any bans that are active.
Default Aliases
(notice:full client users must be logged-in)
| Alias Name | Command | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
| /j | /join $1- | Smaller command to join channels |
| /cs | /msg ChanServ $1- | Message ChanServ with only two letters. |
| /ns | /msg NickServ $1- | Message NickServ with only two letters. |
| /bs | /msg BotServ $1- | Message BotServ with only two letters. |
| /ms | /msg MemoServ $1- | Message MemoServ with only two letters. |
| /os | /msg OperServ $1- | Message OperServ with only two letters. |
| /voice | /mode # +v $1 | Voice a user/nick |
| /devoice | /mode # -v $1 | Remove voice from a user/nick (/unvoice is the same) |
| /ban | /mode # +b $1 | Ban a user/hostmask (/ban<space> = show list with unban buttons) |
| /unban | /mode # -b $1 | Remove a ban from a user/hostmask (/deban is the same) |
| /op | /mode # +o $1 | Give operator status to a user/nick. |
| /deop | /mode # -o $1 | Remove operator status from a user/nick (/unop is the same) |
| /halfop | /mode # +h $1 | Give half-operator status to a user/nick. |
| /dehalfop | /mode # -h $1 | Remove half-operator status from a user/nick (/unhalfop is the same) |
| /admin | /mode # +a $1 | Give super-operator status to a user/nick (called Admin on Mibbit, use "/raw admin" for the ircd command) |
| /deadmin | /mode # -a $1 | Remove super-operator status from a user/nick (/unadmin is the same) |
| /owner | /mode # +q $1 | Give owner status to the user/nick |
| /deowner | /mode # -q $1 | Remove owner status from the user/nick (/unowner is the same) |
| If you made any changes to your prefs before these defaults were moved from the backend you have to add the defaults you are missing manually or (if your changes were only minor) do a "Reset all to defaults" |
Multi-Mode Aliases
In Chatzilla, you can do /voice Nick1 Nick2 Nick3 Nick4 (ect) and they all become voiced. The alias showing is the closest to that.
Match:
/muvoice /mudevoice /muop /mdeop (ect.)
Command
/mode # [+/-][mode] $1 | /mode # [+/-][mode] $$2 | /mode # [+/-][mode] $$3 | /mode # [+/-][mode] $$4
Replace [+/-] with either a + or a - and [mode] with a mode of your choice, like v (voice), h (halfop), o (operator), a (super-op or admin), or e (exempt)
Some common examples are:
/mode # +v $1 | /mode # +v $$2 | /mode # +v $$3 | /mode # +v $$4 /mode # +o $1 | /mode # +o $$2 | /mode # +o $$3 | /mode # +o $$4
Usage:
/muvoice Havvy Molkmin Hercule
Output:
+++ yourNick has voiced Havvy +++ yourNick has voiced Molkmin +++ yourNick has voiced Hercule